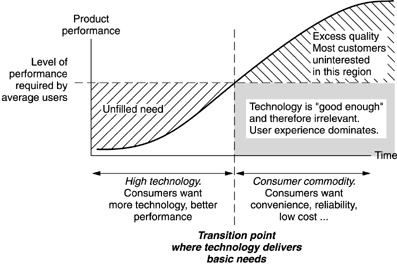
Knowing something about behavior, visual processing, and human nature, designers can nudge users into doing the right (or in this case, lawful) action. Speeding is a problem all over the world. People are notorious for underestimating the real amount of time it takes to get places they need to be. Traffic congestion, car problems, detours, and other (un)foreseen events can make a huge difference in time variability of getting from one place to another. The problem, though, is that we can’t really force people to leave on time or drive the speed limit when the drivers think that no one is looking. So with the law on our side, we can create other ways of forcing people to behave lawfully by changing environmental conditions and relying on human nature not to do what’s right, but to do what they think they have to based on circumstance. Here are a few creative ways of solving the speeding problem on our streets. Using Visual Processing Errors to Slow Traffic Canadian drives misdiagnose the problem and try to drive straddling the “hole” in the road. Everyone is successfully slowed down. The Fake Traffic Cop Threat as a Speeding Deterrent In general, people tend…