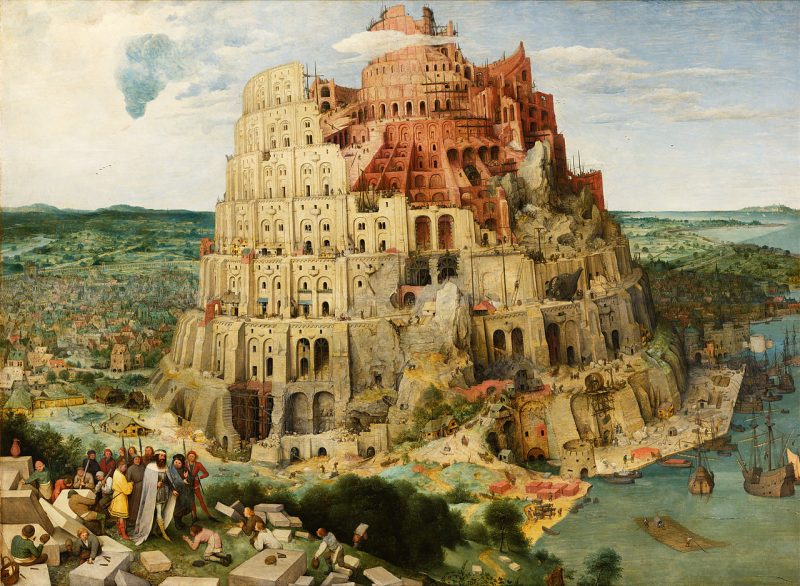
Recession is an interesting prism by which to examine our modern society. The scarcity of jobs a century ago, led to an abolishment of child labor, an extension of the educational system to accommodate these out-of-work children, and a development of new laws to serve them. Most importantly, dire economic conditions were the direct cause behind the “discovery” of a new stage of life: adolescence. The current economic hardship is particularly difficult on the 18 to 30 demographic. These “adults” are struggling to find jobs, life-long relationships, educational opportunities, and self-fulfillment. The term failure to launch is coined to describe the restlessness and ambiguity felt by this population. Dr. Jeffrey J. Arnett describes this phase of life as emerging adulthood: “Instead of entering marriage and parenthood in their very early twenties, most people now postpone these transitions until at least their late twenties, and spend their late teens through their mid-twenties in self-focused exploration as they try out different possibilities in love and work. Essentially, a new developmental stage has been created between adolescence and young adulthood.” [http://www.jeffreyarnett.com] Dr. Arnett discusses the internal traits that define his newly-proposed phase of life: identity exploration instability in work, relationships, living circumstances self-focus…
There's a word for that?
A Dictionary of Cool Words That Hide True Feelings & Meanings from Parents Many of the strange vocabulary words, that…
Read more →