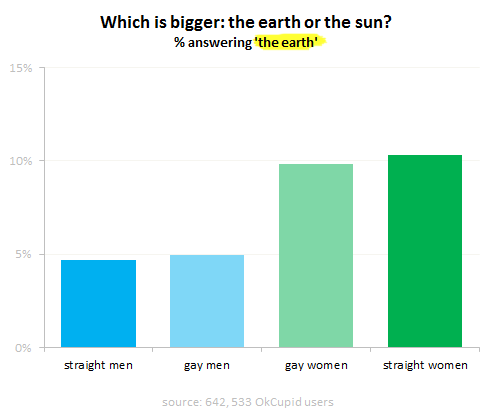
I’ve been using the p-prim ever since I’ve learned of them, back in my graduate school days at UC Berkeley. P-prims stand for phenomenological primitives and were “invented” by Andrea diSeesa, a UC Berkeley professor in the School of Education who also happens to be a physicist (diSessa, 1983). Visit his Wikipedia page and check out some of the cool projects he’s working at now. Before I give a definition of a p-prim, I think it would be good to give a few examples. Here’s a graph published by OkTrends on beliefs of various groups (in this case as defined by their sexual orientation) about the relative size of our sun versus the Earth (our planet). Even disregarding the differences in percentages due to sexual preference, an awesome 5 % to 10 % of our population believes that the planet we live on is larger than the star it orbits. Would this qualify as a p-prim? Yes: it’s not a formally learned concept; it describes a phenomenon; it’s a bit of knowledge based on personal observations: the sun looks like a small round disk in the sky; it’s a useful problem-solving tool when one has to draw a picture with…