
How does one design a successful ad? That depends on the culture at which the ad is aimed. Here are a few example of ketchup ads. Spot the one NOT aimed at an American audience!
What does the product do?
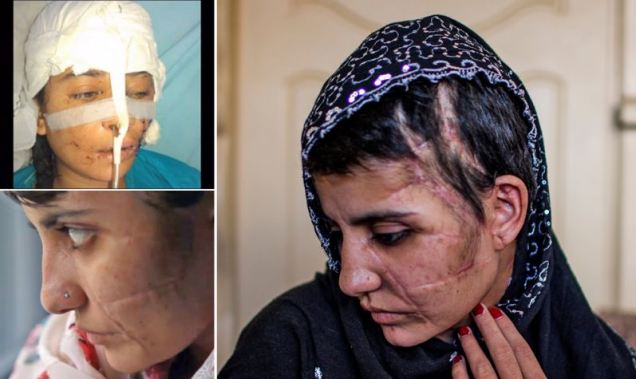
On the same day as I read about Gul Meena — a 17 year old Pakistani girl who was almost killed and severely maimed by her own brother — I bought a pair of skinny jeans. When I got home, I noticed they were made in Pakistan. I think I don’t need to say more… Gul Meena, 17, left her abusive husband in Pakistan for another man. Meena’s brother hacked her friend to death with an ax, before turning on her. Skinny Jeans Made in Pakistan
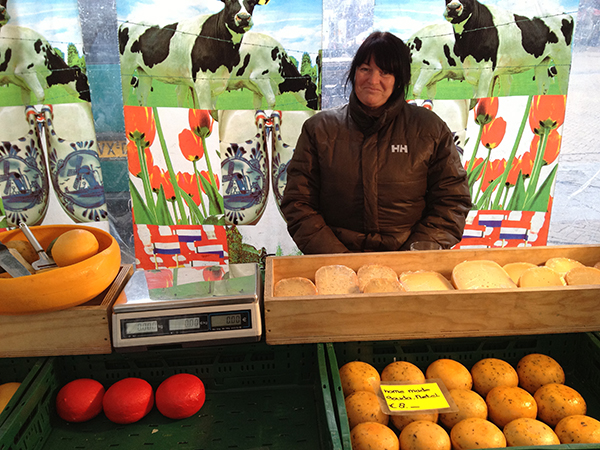

I just returned from a brief visit to The Hague and Amsterdam. When in a foreign country encountering an unfamiliar language, it’s easy to focus on the visual presentation of content since the linguistic portion of the presentation is unavailable for processing. People who can read can’t help but do so when presented with text. But when one can’t process the linguistic content, all that is left are visual clues (and smells and sounds…). So I took a few snapshots to show how the tone of the interface impacts the emotional processing of content and attitude of the customer to the content. Selling Cheese in Amsterdam This is a farmers’ market stall in the middle of Amsterdam, selling home-made cheese. The woman in the photo is the actual cheese maker. Note the hand-lettered signs, the simple wooden boxes, the plain presentation — the overall effect is home made goods, care in production, quality product, even made with love. Fancy production values would just be off putting in this context, and probably result in lower sales of cheese. This NOT a museum, but rather a neighborhood cheese store in Amsterdam. (It is located next door to the flower museum…). What is…
How we think about problems depends in part of how we are taught to do so. And that education is seeped in our culture and language. Metaphors, mnemonics, analogies, riddles, word choice for explanations are tightly interwoven into our language. Just like it was probably impossible for Romans to invent calculus given their numeral system, it is difficult to think clearly about some problems in some languages. I’ve learned advanced physics and mathematics in English and find it very difficult to express thoughts in those domains in Russian (my native language). But when I first came to New York, I marveled at how poor my cohorts’ geometry proofs were — their presentations took a lot of space and too many steps to achieve what I was taught to do in minimal configuration. I was taught to jump and bound from concept to concept (in geometry), while the students in America were taught to crawl through ideas. I found that maddening! But it was a different math language, and as such it allowed for a different set of affordances… It is difficult to easily show the differences in thought process that language makes in this short blog. But here’s a bit…

I get a lot of email forwards…don’t we all? And just the other day I got one that I have seen many times already over the past few years… Usually, you look, you smirk, you move on. But this time, the photo got me thinking: that poor kid — he has no memory of this shot, but he will be remembered for it for the rest of his life! The shot has long ago slipped from the close circle of sharing that his parents intended it for and has been widely distributed through out the world. Someday, this kid might even get it as mail forward himself: an adult man looking at a silly embarrassing moment that got away… Information with Expiration Date Somehow, I don’t imagine that getting “an image that got away” of oneself would be a source of continuous pleasure. One might want to forget the whole thing… And it is not just images — although having images with expiration dates would be very valuable — there are loads of information that should be forgotten by design. When my generation was growing up, the silly and stupid things we did didn’t end up as data for public…
We have to work within the boundaries of what’s possible given the history of the social system, the constraints of technology, the limitations of budgets, and cultural limits of the society wich endevers to implement the socio-technical system.