Judson, O. (2009). “A Language of Smiles.” New York Times. Retreived on 30 June, 2010 http://opinionator.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/10/27/a-language-of-smiles/?hp Summary: This article explores the possibility that languages which require a speaker to move his/her mouth in particular ways predisposes the population which speaks that language to be either happy or gloomy. This article begins by explaining that the idea that physically moving the corners of one’s mouth up into a smile or down into a frown can literally altar one’s mood is not a new idea. Literary authors such as Edgar Allen Poe and scientists such as Charles Darwin have made references to that idea in their works. However, data (I can only assume that by “data” the author means statistical or scientific data) has been accumulated only in the last 30 years. Why the ways in which one moves his/her mouth can affect one’s mood is not certain. Two possible explanations are: 1) it is a matter of classical conditioning such as Pavlov’s dog (who was conditioned to salivate whenever he heard a bell ring because he was taught to associate the bell with the appearance of food), and 2) facial gestures may have an affect on the rate of blood flow to the brain. Different languages require speakers to move their mouths in substantial (and substantially different) ways in…
Tag Archive for user attitude
Cognitive Blindness, Conceptual Design, Contributor, Cultural Bias, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Users
Mining the Web for Feelings, Not Facts
by Andrea Carroll •
Wright, A. (2009). “Mining the Web for Feelings, Not Facts.” The New York Times. Retrieved on 30 June, 2010. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/24/technology/internet/24emotion.html Online presence is a valuable commodity in today’s digital market. As companies seek to track exactly how their brand is discussed via the web and where these discussions appear, it becomes apparent that even a team of employees devoted to such research cannot tackle the shear size of the medium. Thus, algorithms are being employed by marketing research firms as well as companies themselves to handle not only the amount of information present on the Internet, but also in what context it amasses. These algorithmic tools are applied all over the web, but are concentrated on social networking sites like Facebook and Twitter, as well as sites that allow large amounts of user-generated content. Theoretically, in this way a computer can track not only when a company is mentioned but also in what connotative context it appears. Differing from previous brand tracking, these new programs seek to determine subjective opinion as well as objective knowledge. By programming computers to scan the Internet for words that hold certain connotative meanings, marketers and brands can preemptively address user satisfaction issues as well as…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Users
Response to ‘Young More Lonely Than the Old’
by vhood •
Murphy, C. (2010). “Young More Lonely Than The Old,” BBC News. Retrieved on 2010/05/25. http://news.bbc.co.uk/go/pr/fr/-/2/hi/health/8701763.stm Summary: Clare Murphy suggests the young tend to feel lonelier than the old in the UK. What does the article mean by ‘lonely,’ and what are the factors that contribute to Britain’s youth to feel such an emotion? England’s elderly and youth feel two different types of loneliness. Elderly loneliness derives from the isolation caused by the decomposition of the nuclear family, as well as long life expectancy. Youth loneliness is caused by modern day living. Today, more focus is placed on careers rather than on the public community. Thus, individuals exert more energy into their work than into building community ties. Social network sites, a technology invention of the youth’s era, incredibly connect hundreds and thousands of people across the globe. Communication through these sites, however, does not produce the same satisfaction of face to face interaction. Thus, one may find they have a plethora of friends on their social network site, but very few that they can have a person to person contact with. Lastly, urban planning greatly affects how social is a community. The urban planning of London encourages a far lesser…
Background Knowledge, Background Knowledge Errors, Cognitive Blindness, Contributor, Cultural Bias, Cultural Differences, Diagnostic Errors, Ethnographic & User Data, Interface Design, Mental Model Traps, Product Design Strategy, Users
A Curiously French Complaint
by Cecilia •
Kirby, E. (2008). “ A Curiously French Complaint,” BBC News. Retrieved on 2008/12/13. http://news.bbc.co.uk/go/pr/fr/-/2/hi/programmes/from_our_own_correspondent/7779126.stm Summary: This article focuses on the cultural differences between the French and British populations in regards to their medical care. Each culture has their own script of understanding, which people rely to set their expectations during a medical crisis. The author Emma experienced a cultural ‘shock’ during her first encounter with a French doctor due to her vastly different set of expectations. She visits a doctor in France due to the severity of a sore throat, where she is “diagnosed with a severe lung infection, mild asthma and had in my hand a prescription for six different types of medicine, an appointment at the local hospital’s radiology department and an emergency referral to a specialist in pulmonary disease (article).” Upon her return to Britain a few days later, she visits her family physician, who within a few minutes diagnoses her with only a ‘common cold.’ Her article then explains how the French expect a much more sever diagnosis to support their physical suffering. France is also the leading country of consumers who take prescription medications. While in England, there’s a more ‘keep a stiff upper lip’…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Perception, Product Design Strategy
On “‘Ringtone Therapy’ Sweeping Mobile Phone-Mad Japan” by Buerk
by Anne •
Buerk, R. (2010). “Ringtone Therapy Sweeping Mobile Phone-Mad Japan.” Retrieved 23. August, 2010: http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/8591845.stmhttp://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/8591845.stm Summary: Buerk lets the world in on a new craze sweeping across Japan—a country known for being on the frontier of technological innovation. What’s the craze? Ring-tone therapy! The Japan Ring Tone Laboratory run by Matsumi Suzuki is producing ring-tones which they claim have therapeutic uses. One such tone touts the ability to dislodge pollen from a user’s nose by holding the handset to the nose while the ring-tone plays, another can help one lose weight, and another helps insomniacs fall asleep. Index, Japan’s mobile phone content provider acknowledges there is no proof that these therapeutic ring-tones actually work, but they note that people must believe in their effectiveness due to the large amount of downloads. The therapeutic ring-tone works by playing a tone emitted from the handset of the cell-phone. Depending on the ring-tone the therapeutic effect is different. If one has allergy problems, they can download and play a ring tone, place it up to their nose and it will in principle dislodge the pollen from the nose, reducing allergy symptoms. If one is having sleeping problems, another ring-tone once downloaded onto the cell…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Ethnographic & User Data, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Users
Study: Long Road to Adulthood Is Growing Even Longer
by Theresa Bruketta •
Cohen, P. (2010). “Long Road to Adulthood Is Growing Even Longer.” The New York Times. Retrieved on 23 June, 2010. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/13/us/13generations.html Summary: Recent studies and surveys reveal the shift to adulthood in the United States is occurring later in life and that traditional markers of such a transition are also being reconsidered. Finishing one’s education, becoming financially independent – these milestones are still associated with people in their late teens and early twenties. However this article suggests these milestones, for many people, are now not being met even in their 20s or 30s. Marriage and having children are happening much later in life on average or are not happening at all. While getting married or having children is now more commonly viewed as a lifestyle choice, pursuing higher education is more common than ever before. Pursuing more education and professional opportunities are cited as factors in causing this shift. As the average age for one’s first marriage has shot up across all ethnic and income groups, the number of children born outside of marriage is at 40 percent, up from 28 percent in 1990 showing that this shift is broad and it’s redefining adulthood not only in terms of when…
Attention, Conceptual Design, Contributor, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Personality, Product Design Strategy, Users
Ch-ch-ch-ch-changes: Interview with David Bowie
by AnneMalhotra •
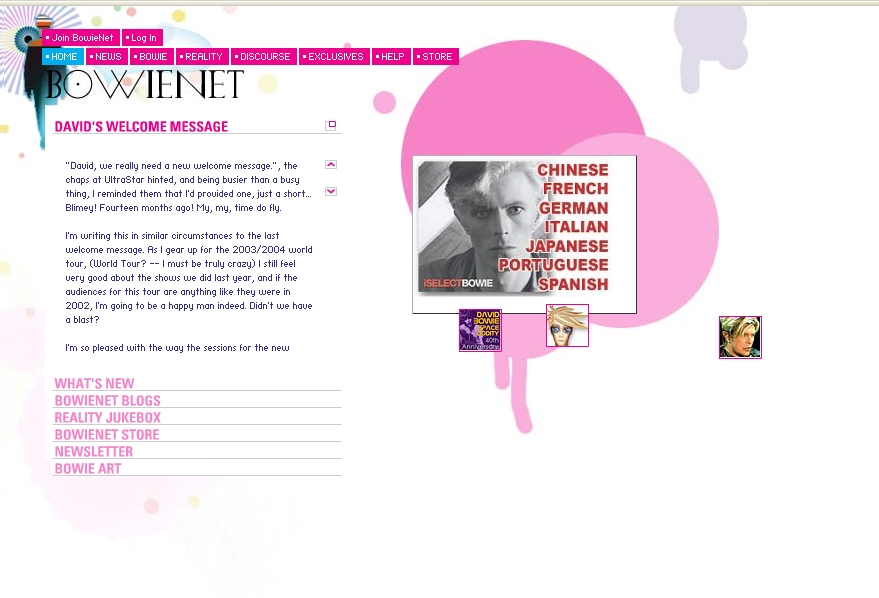
Nash, K. (1999). “Ch-ch-ch-ch-changes: Interview with David Bowie.” ComputerWorld. Retrieved August 1, 2001: http://www.computerworld.com/cwi/story/0,1199,NAV47-STO39387,00.html The is a screen shot of David Bowie’s Home Page as it appeared on June 24th, 2010. In this interview, David Bowie, a musician and philosopher, shares his view of the Internet and how it may evolve and influence society but also the music industry over time. His depiction of his website serves as a starting point to his argument. The individualized portal, BowieNet – where he chats with fans on daily basis and keeps a personal journal – is telltale when it comes to his approach to the net. As a matter of fact, Internet is a huge decentralized village in Bowie’s point of view. The portal – by enabling the creation of online personas and by providing links to all the fan blogs on him – offers the opportunity to foster a village-like facet of internet with a free circulation of information and a sense of community built around him and his music. In fact, such interaction enables, according to Bowie, a new way of knowing people. He confesses that he likes to take on other names to simply observe what happens in the…
