Harmanci, R. (2010). “For digital artists, apps provide new palette.” New York Times Online. Retrieved on October 4, 2010: http://www.nytimes.com/2010/08/20/us/20bciart.html To illustrate the impact of mobile/handheld-device technology on the arts, this article describes the work of several individual artists who have used iPhone/iPad applications as an artistic format. In my overview, I focus on the work by Scott Snibbe and pose the following question: what is it about handheld apps that sets them apart and makes them a more successful environment for interactive art than any other? Scott Snibbe is an artist for whom interactivity, i.e. the opportunity for audience participation, is a central theme. His installations are often designed to capture human bodily actions and respond to them. The audience thus has the experience of bringing an art piece’s content into existence. For example, in Falling Girl (2008) and Make Like a Tree (2006), people’s movements are replicated, with some time lag, by silhouettes projected onto screens, while in Blow-Up (2005) people’s breath triggers fans that reproduce its spatio-temporal contour. Snibbe’s very popular mobile apps are closely based on an earlier Dynamic Systems interactive series that involved manual action, except that their original version used more traditional cursor-based interface. …
Tag Archive for product design
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Perception
Sense of Touch Shapes Snap Judgments
by patrickgary •
Keim, B., (2010). “Sense of Touch Shapes Snap Judgments.” Wired.com. Visited on October 3, 2010: http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2010/06/touching-cognition/ Brandon Keim’s article for Wired.com’s science blog provides a brief overview of recent research into the role that tactile sensations play in human interactions. This new area of psychological research, referred to as Embodied Cognition, could potentially have a significant impact on how we understand social and physical interactions. Put simply, the core findings of the research show that our physical responses to our immediate environment, combined with other factors, can directly and measurably influence our decision-making. One of the examples provided involved giving the subject a heavy clipboard to hold during the experiment; when holding the heavy clipboard, the subjects tended to regard their own opinions and problems presented to them as being more weighty and serious in nature. Other examples showed how a tactile interaction with a rough surface prior to an interview could lead to a harsher attitude towards the interviewee. The article itself is somewhat of a stub, so we are left to imagine the further implications of Embodied Cognition ourselves. What relevance does Embodied Cognition have for product interaction design? After all, it’s not as if touch has previously…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Cultural Differences, Interaction Design, Interface Design
Antisocial Networking?
by Roman Shumikhin •
Stout, H. (2010). “Antisocial Networking?” New York Times Online. Retrieved on 3 October, 2010: http://www.nytimes.com/2010/05/02/fashion/02BEST.html The main topic of this article is that technology may be changing the very nature of kid’s friendships. Children used to actually talk to their friends. But now, even chatting on cellphones or via e-mail is becoming rare. Today’s teenagers and preteens, prefer to make friends and communicate using cellphone texts and instant messages, or through the very public forum of Facebook walls and MySpace bulletins. People now are more likely to use their cellphones to text friends than to call them. The article shows two opposite points of view on the topic. The author believes the quality of human interactions is becoming worse without the intimacy and emotional component of regular face-to-face communications (hence the title of this article). The ease of electronic communication may be making teens less interested in face-to-face communication with their friends, but close childhood friendships help kids build trust in people outside their families, develop empathy, understand emotional nuances and read social cues like facial expressions and body language, and consequently help lay the groundwork for healthy adult relationships. On the other hand, online social networking allows children to become…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Interface Design, Language, Product Design Strategy, Users
Using Menu Psychology to Entice Diners
by Mallika •
Kershaw, S., (2009). “Using Menu Psychology to Entice Diners.” New York Times Online. Visited on October 02, 2010: http://www.nytimes.com/2009/12/23/dining/23menus.html. This article discusses how an understanding of human psychology is being applied to sculpt a restaurant menu into a lucrative tool for the restaurateur. Restaurateurs play down the importance of the cost figure by eliminating the dollar sign and decimals. Adding a personal touch to an item (‘Grandma Mary’s cake’) or a descriptive menu label (‘buttery pasta’) draws more attention to the dish. Other decoys include using a description that glorifies a more profitable dish compared to others. During the tough economic times in the last year, some restaurants were reinventing their restaurants through such menu design techniques, and were hoping that would make the difference they needed. Conceptual design: When you go to a restaurant, good food is not the only thing you seek; you are looking for a good experience. Of course sometimes, great food can make us turn a blind eye to any other inadequacy and draw us back into the restaurant. Nevertheless, a good experience overall manifests itself as a stronger loyalty. If your overall experience has made a lasting positive impression, you may recommend the restaurant…
Anchoring Errors, Background Knowledge, Background Knowledge Errors, Causal Net Problems, Diagnostic Errors, Featured, Mental Model Traps, Metaphor Mistakes, Misapplication of Problem Solving Strategies, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Scaffolding
What is a p-prim?
by Olga Werby •
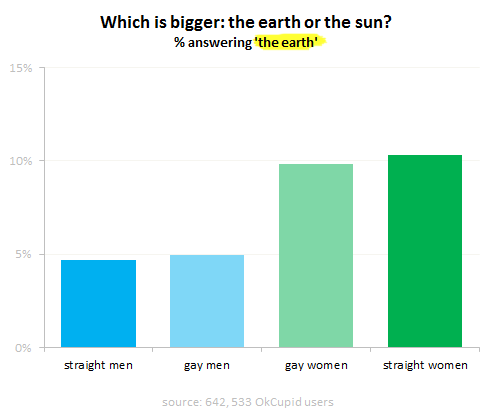
I’ve been using the p-prim ever since I’ve learned of them, back in my graduate school days at UC Berkeley. P-prims stand for phenomenological primitives and were “invented” by Andrea diSeesa, a UC Berkeley professor in the School of Education who also happens to be a physicist (diSessa, 1983). Visit his Wikipedia page and check out some of the cool projects he’s working at now. Before I give a definition of a p-prim, I think it would be good to give a few examples. Here’s a graph published by OkTrends on beliefs of various groups (in this case as defined by their sexual orientation) about the relative size of our sun versus the Earth (our planet). Even disregarding the differences in percentages due to sexual preference, an awesome 5 % to 10 % of our population believes that the planet we live on is larger than the star it orbits. Would this qualify as a p-prim? Yes: it’s not a formally learned concept; it describes a phenomenon; it’s a bit of knowledge based on personal observations: the sun looks like a small round disk in the sky; it’s a useful problem-solving tool when one has to draw a picture with…
Autopilot Errors, Background Knowledge Errors, Conceptual Design, Diagnostic Errors, Errors, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Interruptus Errors, Misapplication of Problem Solving Strategies, Mode Errors, Perceptual Blindness, Perceptual Focus Errors, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Scaffolding, Users, Working Memory
The History of Usability
by Olga Werby •

When did we start being concerned with usability? Some will say that such concern is part of being human: cavemen worked their stone tools to get them just right. Interaction design mattered even then. But the field of usability research really came into being when the tools we used started to run up against our cognitive and physical limitations. And to avoid hitting literal, as well as psychological, walls, it was the aviation engineers who started to think about usability seriously. While cars were becoming ever more sophisticated and trains ever faster, it was the airplanes that were the cause of most usability problems around WWI. Cars were big, but didn’t go very fast or had a lot of roads to travel on at the turn of the century. In the first decade of the 20th century, there were only 8,000 cars total in the U.S. traveling on 10 miles of paved roads. In 1900, there were only 96 deaths caused by the automobile accidents. Planes were more problematic. For one thing, the missing roads weren’t a problem. And a plane falling out of the sky in an urban area caused far more damage than a car ever could. Planes…
Cognitive Blindness, Conceptual Design, Cultural Bias, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Featured, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Mirroring Errors, Pipsqueak Articles, Users
Be the Customer
by Olga Werby •

By our very nature, humans are an “us versus them” kind of mammal. We are quick to judge and categorize: “he’s our kind’a people” or “she’s management.” We adapt and root for our favorite sports teams, sometimes even resorting to violence to “defend our guys.” We peg an art department against the engineers; we side with nurses over doctors; we fight with democrats against republicans; we wave our flags in a spirit of nationalism. And it doesn’t matter if we all work for the same company, heal the same patients, want the same basic rights, or live on a very small planet—we tend to take sides. So it’s no surprise that when product designers develop products the feeling of “us against the users” creeps up into the process. To protect the design process from these “us versus them” impulses, we can create a well-realized user personas based on the the audience taxonomy developed during the conceptual design stage of product design. For each major category in the audience taxonomy, a sample fictional user is created which embodies all of the traits in that audience category: age, profession, socio-economic background, culture and sub-culture, interests and dislikes, family status, education level, etc.…
