Buerk, R. (2010). “Ringtone Therapy Sweeping Mobile Phone-Mad Japan.” Retrieved 23. August, 2010: http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/8591845.stmhttp://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/8591845.stm Summary: Buerk lets the world in on a new craze sweeping across Japan—a country known for being on the frontier of technological innovation. What’s the craze? Ring-tone therapy! The Japan Ring Tone Laboratory run by Matsumi Suzuki is producing ring-tones which they claim have therapeutic uses. One such tone touts the ability to dislodge pollen from a user’s nose by holding the handset to the nose while the ring-tone plays, another can help one lose weight, and another helps insomniacs fall asleep. Index, Japan’s mobile phone content provider acknowledges there is no proof that these therapeutic ring-tones actually work, but they note that people must believe in their effectiveness due to the large amount of downloads. The therapeutic ring-tone works by playing a tone emitted from the handset of the cell-phone. Depending on the ring-tone the therapeutic effect is different. If one has allergy problems, they can download and play a ring tone, place it up to their nose and it will in principle dislodge the pollen from the nose, reducing allergy symptoms. If one is having sleeping problems, another ring-tone once downloaded onto the cell…
Product Design Strategy
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Interaction Design, Perception, Product Design Strategy, Users
On “The Sweet Smell of Morality”
by mwaters •
Humphries, C. (2010). “The Sweet Smell of Morality.” Boston Globe Online, Boston.com. Retrieved on 23 June 2010: http://www.boston.com/bostonglobe/ideas/articles/2010/02/14/the_sweet_smell_of_morality/ Summary: Scientist and Marketers are paying closer attention to the sense of smell. It appears that while once believed subpar to other human senses, the power of smell is being reevaluated. Some studies suggest smell has the power to influence social and moral behavior. Recent findings have found that clean smells perpetuate favorable behavior in instances where someone is in need of help or assistance. This suggests that smells, known for their influence on emotion and memory, might also have an effect on thought. Additional studies have shown that consumers shopping habits, such as where to shop and how much to buy, are influenced by smell, having more to do with choice than mood. Using smell as a lure might sound manipulative, yet some researchers claim we are aware of scents and are not deceived by them. Marketers are currently looking into ways to incorporate smells into brand recognition. It’s possible for humans to undergo training to perfect their sense of smell. As more knowledge comes about regarding smell, and the complexities of this sense are realized, consumers can expect to be…
Attention, Conceptual Design, Contributor, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Personality, Product Design Strategy, Users
Ch-ch-ch-ch-changes: Interview with David Bowie
by AnneMalhotra •
Nash, K. (1999). “Ch-ch-ch-ch-changes: Interview with David Bowie.” ComputerWorld. Retrieved August 1, 2001: http://www.computerworld.com/cwi/story/0,1199,NAV47-STO39387,00.html The is a screen shot of David Bowie’s Home Page as it appeared on June 24th, 2010. In this interview, David Bowie, a musician and philosopher, shares his view of the Internet and how it may evolve and influence society but also the music industry over time. His depiction of his website serves as a starting point to his argument. The individualized portal, BowieNet – where he chats with fans on daily basis and keeps a personal journal – is telltale when it comes to his approach to the net. As a matter of fact, Internet is a huge decentralized village in Bowie’s point of view. The portal – by enabling the creation of online personas and by providing links to all the fan blogs on him – offers the opportunity to foster a village-like facet of internet with a free circulation of information and a sense of community built around him and his music. In fact, such interaction enables, according to Bowie, a new way of knowing people. He confesses that he likes to take on other names to simply observe what happens in the…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Cultural Differences, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Product Design Strategy, Users
Can Design Change the World?
by Andrea Carroll •
Tanneeru, M. (2009). “Can Design Change the World?” CNN online. Retrieved June 23, 2010. http://edition.cnn.com/2009/TECH/11/06/berger.qanda/index.html Summary: CNN talks to Warren Berger, who wrote the book “Glimmer: How Design Can Transform Your Life and Maybe Even the World” about how greater communication through design can change the world. He shies away from speaking of this change in grandiose terms, seeking to differentiate his idea as one that stems from design’s problem-solving capabilities on a case-by-case basis. Berger asserts that design, at its core, is more than making products or spaces look good, but rather, it seeks to identify a problem or an unaddressed need and solve it through a trial-and-error process. It involves studying people and the way that they live to pinpoint ways in which their lives could be made better. This is done through much brainstorming, prototyping, and audience testing. The Internet has drastically changed the ways in which designers work, collaborate, and even identify themselves as designers. Widespread access to information has meant that knowledge can be passed on from one person to another at a quicker rate—meaning that one person’s mistakes can be learned from and not repeated. Social networking groups allow designers to connect to share…
Attention Controls Errors, Cognitive Blindness, Featured, Misapplication of Problem Solving Strategies, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Scaffolding
Neuro-Parasites & Problem Solving Errors
by Olga Werby •

Dr. Robert Sapolsky is a professor of neurobiology at Stanford University. He started his career studying baboons, charting the relationship between stress hormones and an individual animal’s social ranking in the baboon society hierarchy. The lower the rank, the more stress the animal experiences, the more consequences there are to the health outcomes and longevity of the baboon. Making a parallel to human society, the conclusions of Dr. Sapolsky’s study is that it sucks to be at the bottom of the social order. In his books “Primate’s Memoir” and “Zebras Don’t Get Ulcers,” Dr. Sapolsky provides copious details of his work and his conclusions. (see Recommended Books for details) But residing on the bottom of the social ladder is not the only problem a mammal like us can experience. In his video interview with Edge (www.Edge.org), Dr. Sapolsky describes the adventures of Toxoplasma–a protozoan parasite carried by cats which causes an infection Toxo–in our amygdala. Post an active infectious state, Toxo is able to manipulate human dopamine levels. People with the post-Toxo infection have higher than normal dopamine levels, resulting in some interesting cognitive consequences. There’s been solid research that documents a high level of Toxo infections in schizophrenic patients. There…
Conceptual Design, Contributor, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Product Design Strategy, Users
Reinventing the wheel to help disabled.
by BrentM •
Article: Elliot, J. (2008). “Reinventing the wheel to help disabled.” BBC NEWS. Visited on 5 September 2008 http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7475609.stm Summary: Wheelchair wheels are not optimally designed for wheelchair users who must travel. While the wheels may be removed from a folding wheelchair, they do not themselves pack well and must often be checked in on flights or stowed separately from the folded chair in other travel scenarios. Former Royal College of Arts (RCA) student Duncan Fitzsimons designed a folding wheel for bicycles and is modifying the design to work for wheelchair users. His design, which folds the full-sized wheel flat while allowing use of a regular tire and inner tube, gives the wheelchair user the ability to quickly stow their chair when using other modes of transportation. Conceptual design: Wheelchair wheels must be removed from wheelchairs, even folding models, to be stowed when traveling. Design a wheel which does not require removal from the chair and significantly reduces the amount of space needed to stow the chair. Interaction design: The wheel must be large, as this is the key to a wheelchair user’s independence. It should be designed to fit different budgets and performance needs. It must fold flat so it may be…
Ethnographic & User Data, Interface Design, Perceptual Focus Errors, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Users
Understanding Complex Visual Information…
by Olga Werby •
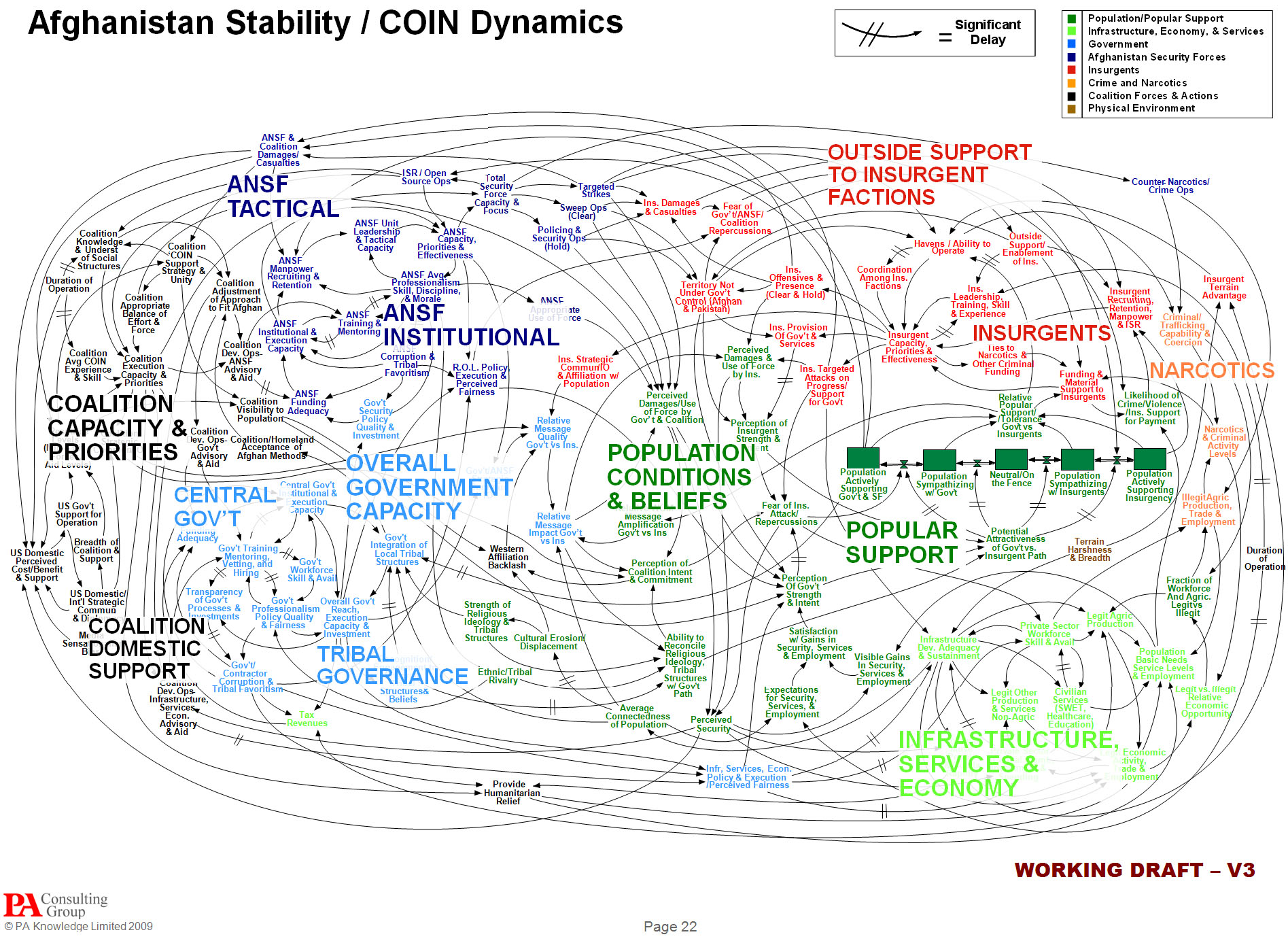
…or not comprehending it, as the case may be. A few years ago, I wrote a paper about people’s ability to comprehend complex visual information such as graphs, charts, diagrams, maps, and so on. Intuitively, we are culturally-trained to believe that it’s much easier to extract information from a picture than from text. But upon testing this belief (p-prim, for those in the know), I found that contrary to the notion “a picture is worth a thousand words,” it’s much more difficult to get data from an illustration than from a story. While emotional impact might be larger with a picture, it’s not true for comprehension. You can read the results of my study at http://www.pipsqueak.com/pages/papers.html “Visual Symbolic Processing in Modern Times” paper presented at AACE ED-MEDIA Conference in 2008. Since then, I’ve collected more data, and the results are similarly aligned: problem-solving requiring higher level visual symbolic processing skills is difficult and results in communication failures. A secondary, and surprising, finding was a gender discrepancy in performance outcome testing of visual symbolic processing skills. Higher level and lower level visual symbolic processing are defined in the paper. And anyone interested in testing their visual processing skills are welcome to…
