Kershaw, S., (2009). “Using Menu Psychology to Entice Diners.” New York Times Online. Visited on October 02, 2010: http://www.nytimes.com/2009/12/23/dining/23menus.html. This article discusses how an understanding of human psychology is being applied to sculpt a restaurant menu into a lucrative tool for the restaurateur. Restaurateurs play down the importance of the cost figure by eliminating the dollar sign and decimals. Adding a personal touch to an item (‘Grandma Mary’s cake’) or a descriptive menu label (‘buttery pasta’) draws more attention to the dish. Other decoys include using a description that glorifies a more profitable dish compared to others. During the tough economic times in the last year, some restaurants were reinventing their restaurants through such menu design techniques, and were hoping that would make the difference they needed. Conceptual design: When you go to a restaurant, good food is not the only thing you seek; you are looking for a good experience. Of course sometimes, great food can make us turn a blind eye to any other inadequacy and draw us back into the restaurant. Nevertheless, a good experience overall manifests itself as a stronger loyalty. If your overall experience has made a lasting positive impression, you may recommend the restaurant…
Interface Design
What does the product feel and look like?
Ethnographic & User Data, Featured, Interface Design, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy
Emotional Design
by Olga Werby •
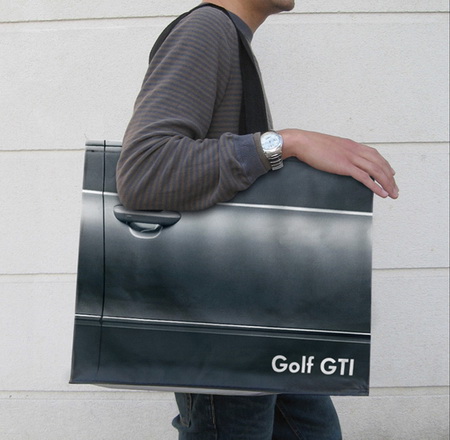

Product design is not just about usability. How we feel about a product makes a lot of difference. The research shows that two identical applications—with similar failure rate, but with a different take on dialogue box writing—result in very different perceptions of usability by its audience. The application with polite dialogue text always wins. Emotional design deals with how we feel about the product. Interfaces design is all about the look and feel and is responsible for a large portion of generated user emotions. Here are some examples of bag designs. If you want to encourage recycling, this is a great way of making these bags valuable—the users won’t throw them out after one use. Enjoy!
Errors, Ethnographic & User Data, Interface Design, Perception, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Scaffolding, Users
Accidentally Supergluing an Eye Shut
by Olga Werby •
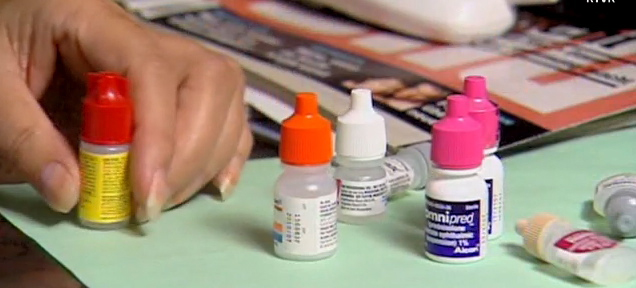
I hope the mere reading of the title made you queasy—it makes me shudder every time. On October 6th, CNN posted a story about a woman from Phoenix, Arizona, who accidentally put drops of super glue into her eye instead of the eye medication. She called 911, and in the emergency room the doctors had to cut open her eye and peel the hardened layer of super glue from her eye ball. If this doesn’t make you sick, then… One may ask: how stupid does one have to be to glue their eye shut? But, as with many other product-use errors, the woman made a very common mistake. The hospital wasn’t surprised—apparently these accidents happen all the time. Because of poor vision, she couldn’t distinguish between the bottles of her eye medicine and the package of super glue. Take a look at this: If you are relying purely on feel, the woman’s error no longer feels so outlandish. Here’s what she probably could see with her poor vision: And here is what we, the well-sighted, could see: So upon a close examination, the woman’s error is a natural mistake. (Yeah, I know, I know: Why would she keep the bottle…
Autopilot Errors, Background Knowledge Errors, Conceptual Design, Diagnostic Errors, Errors, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Interruptus Errors, Misapplication of Problem Solving Strategies, Mode Errors, Perceptual Blindness, Perceptual Focus Errors, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Scaffolding, Users, Working Memory
The History of Usability
by Olga Werby •

When did we start being concerned with usability? Some will say that such concern is part of being human: cavemen worked their stone tools to get them just right. Interaction design mattered even then. But the field of usability research really came into being when the tools we used started to run up against our cognitive and physical limitations. And to avoid hitting literal, as well as psychological, walls, it was the aviation engineers who started to think about usability seriously. While cars were becoming ever more sophisticated and trains ever faster, it was the airplanes that were the cause of most usability problems around WWI. Cars were big, but didn’t go very fast or had a lot of roads to travel on at the turn of the century. In the first decade of the 20th century, there were only 8,000 cars total in the U.S. traveling on 10 miles of paved roads. In 1900, there were only 96 deaths caused by the automobile accidents. Planes were more problematic. For one thing, the missing roads weren’t a problem. And a plane falling out of the sky in an urban area caused far more damage than a car ever could. Planes…
Cognitive Blindness, Conceptual Design, Cultural Bias, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Featured, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Mirroring Errors, Pipsqueak Articles, Users
Be the Customer
by Olga Werby •

By our very nature, humans are an “us versus them” kind of mammal. We are quick to judge and categorize: “he’s our kind’a people” or “she’s management.” We adapt and root for our favorite sports teams, sometimes even resorting to violence to “defend our guys.” We peg an art department against the engineers; we side with nurses over doctors; we fight with democrats against republicans; we wave our flags in a spirit of nationalism. And it doesn’t matter if we all work for the same company, heal the same patients, want the same basic rights, or live on a very small planet—we tend to take sides. So it’s no surprise that when product designers develop products the feeling of “us against the users” creeps up into the process. To protect the design process from these “us versus them” impulses, we can create a well-realized user personas based on the the audience taxonomy developed during the conceptual design stage of product design. For each major category in the audience taxonomy, a sample fictional user is created which embodies all of the traits in that audience category: age, profession, socio-economic background, culture and sub-culture, interests and dislikes, family status, education level, etc.…
Background Knowledge Errors, Conceptual Design, Errors, Ethnographic & User Data, Interaction Design, Interface Design, Mental Model Traps, Mirroring Errors, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Users
Metacognition Failure: If I find it easy, it must not be important
by Olga Werby •

Making something easy to understand is extremely difficult. A good designer knows this, knows how hard one has to work to make something comprehensible and easy to use. Unfortunately, users and consumers of products (including education) tend not to get it. We live in society ruled by “More is Better” p-prim: more stuff is better, more money is better, more food is good, more medication is great…more, more, more. Movies, television, newspapers, magazines, all reinforce this idea in our minds. We live in a “super-size me” world. But this basic decision-making algorithm leads to very faulty reasoning. There are multiple corollaries to the “more is better” axiom: thick books without graphics are more educationally valuable, more important (this is based on research I did many years ago with 5th graders); longer essays are clearly better and should get higher graders (the students worked harder/longer on them); big words are better than small ones in expressing ideas (thus we get very pretentious writing); work should be judged by the time it took to complete and not by the quality of the results it produces; more expensive clothes (cars, stereos, etc.) are clearly more valuable (this is a true statement, but most…
Cognitive Blindness, Errors, Featured, Interface Design, Perception, Pipsqueak Articles
Color Blind Design
by Olga Werby •
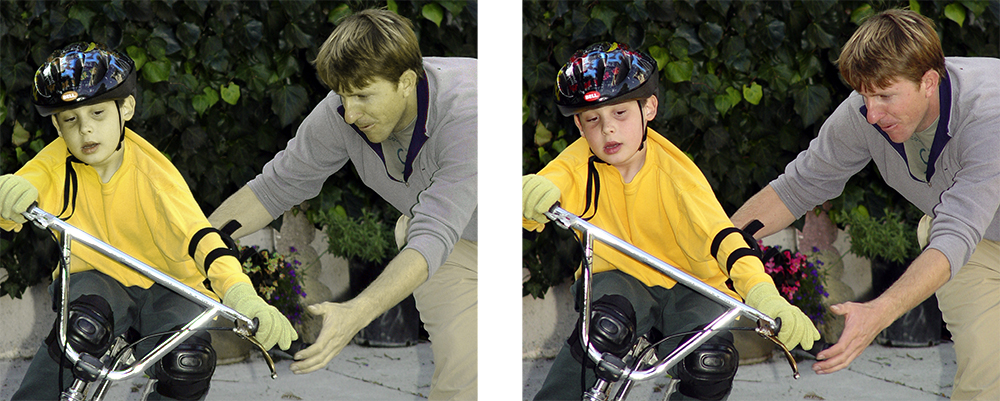

Do you see any difference between these two images? About 10% of the male population (with up to 20% among some ethnic groups) do not. Do differences in the way individuals perceive and process color information matter? Sometimes… Consider this informational graphic: It’s easy to see how the information contained within this chart has been transformed and no longer carries the same meaning. Which is the right one? When designing information for communication, it’s important to consider the totality of the intended audience: What are their strength? What are their limitations? Like cognitive traits, perceptual differences have to be accommodated by good design. Some issues that individuals with deuteranope deficit (red/green confusion) face is inability to tell the difference between colored items that are too thin (lines), point sources, and blinking lights (think traffic lights blinking green or yellow). These problems effect real-life performance and can lead to accidents: think traffic light color confusion. It is the job of a product designer to reduce the difficulties these individuals face. You can use this URL to check your site for color blind usability: http://www.vischeck.com/vischeck/vischeckURL.php
