My grandmother grew a “mushroom” in her kitchen, feeding it tea and sugar. It had a slightly sickly sweet smell and it was hard and springy to the touch. I never liked to drink the stuff, but I always considered it somewhat of a family pet (I never had a dog or cat, being allergic to both). Years later, a friend game a small batch of mother culture grown in black tea—”That’s the stuff,” I thought! I kept growing it for a few years, with my family extremely squeamish even at the thought of it living in our kitchen. But I liked it, it felt like a bit like having grandma in my kitchen. It lived for about 4 years, and then died when we left it alone for a few weeks while we traveled on vacation. My boys were thrilled. Recently, I’ve read that Google has been growing these in green and black tea varieties for their employees cafeteria—apparently, it’s in fashion again. And now I came across a video below: Now that’s truly being fashionable!
Cultural Bias, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy
Cultural World Domination
by Olga Werby •

When we first arrived in New York as Russian refugees many, many years ago, everything was so confusing. I remember lying on the bed in a hotel room somewhere in Brighton Beach, Brooklyn, with my whole family (mother, father, sister, and me) and watching commercials on TV. There was a stick figure running around the screen screaming “Cherio-o-o-o-o-o-o-o-s.” We debated for hours trying figure out what it was about. And then there was a time when my parents let me buy a bag of Cheetos. I almost vomited when I tried one—in Russia, things that looked like that were sweet. The complete mismatch between my expectations and the actual taste made me gag. To this day, I hate the stuff! So when companies are on the path of world domination with their products, understanding cultural differences in background knowledge, perceptual expectations, preferred ways of doing things is a must. To see how some giants customize their products to make them more culturally sensitive, I took a look at McDonalds‘ menus from around the world. Check it out: Note: I went looking for the old Cheerios commercial, but could only find this one—it’s close, but the one we saw didn’t have…
Conceptual Design, Cultural Differences, Ethnographic & User Data, Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Users
Demonstration of Wealth
by Olga Werby •

People have been flashing “bling” around since the cave days. But what we perceive as “bling” has changed dramatically over the years and over cultures. We are social animals, we put a lot of value in our place in the social hierarchy of the group. By demonstrating wealth, we are advertising our social status in the community. Body Image How can you tell how much influence a cave man had in his group? Well, one was probably the way he looked: body paint, tattoos, scarification, body modification, hairdos, teeth filings, nail beautification, and accessories. And while somethings were transitory—beads are easily lost in battle, nails broken during a hunt—some are permanent status symbols. When all you owe is carried on you, then permanent modifications is a good solution to broadcasting your importance and achievements to the group. Each scar carries meaning and is much easier to show off than notches on the bed post. But body modifications is a very painful bling. Products Once the society is a bit more stable, stuff becames a preferred way of social display. Jewelry can be worn, homes can be owned, cars can be seen—there are many ways to show off wealth in the…
Background Knowledge, Conceptual Design, Cultural Bias, Interface Design, Pipsqueak Articles, Reference
Evolutionary Theory of Beauty
by Olga Werby •
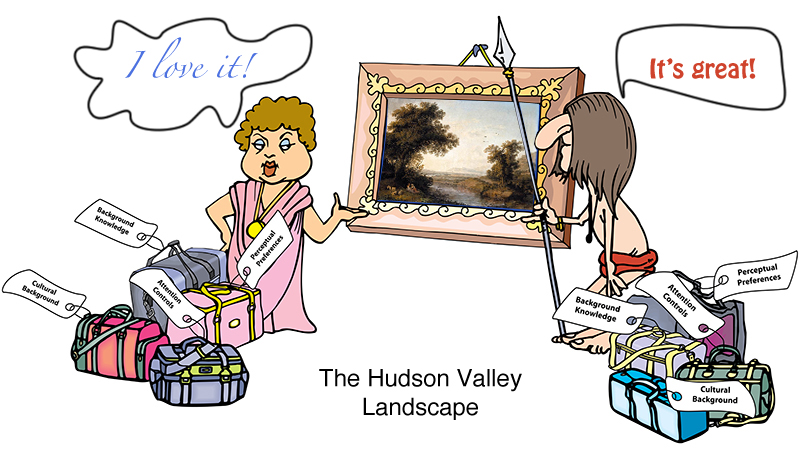
David Brooks: The Social Animal I just finished reading a book by David Brooks, “The Social Animal.” While initially hesitant, I really enjoyed reading it. The book, a fiction, bundles together a lot of interesting information on the latest (and not so latest) advances in our understanding of the workings of the human mind. So it’s easy to see why I would like it! While there are many ideas worth considering in the book, I picked a small detail mentioned in passing: the evolutionary pull towards the love of a “Hudson Valley Landscape.” The Hudson Valley Landscape has the following features: The landscape has lots of open space interspersed with tall vegetation. There’s a far horizon that defines the space: a valley, a glade, a river basin, a farm, etc. There’s a clear evidence of fresh water: a river, a stream, a pond, etc. There are a few large trees in the foreground, offering shade, fruit, safe escape, or all of the above. There’s a path from the foreground to the background. There are people and man-made structures visible somewhere. There are “safe” animals or birds visible: cows, ducks, deer, etc. Amazingly, all cultures respond positively to this genre of…
Attention Controls Errors, Perception, Perceptual Blindness, Pipsqueak Articles
Attention Control Errors & Perceptual Blindness
by Olga Werby •
Harvard Vision Lab created a few experiments that feature Attention Controls Errors and Perceptual Blindness. Below is one of their optical illusions. Directions: concentrate on the central white dot. Did the colors of the outside dots continue to shift throughout the video? If they stopped when the dots were rotating, then you’ve just experienced Silencing—the lab’s vocabulary for individual’s inability to pay attention to both motion and color shift at the same time. Here, we mostly call it Perceptual Blindness. My Personal Experience with this Illusion: The first time I watched the video, I think the colors stopped shifting…but I don’t really remember—I wasn’t paying attention! The second time, I saw the shift. When I showed the illusion to a colorblind individual, he saw the shift from the first viewing. To read about the complete experiment and to view more illusion videos, please visit the lab: http://visionlab.harvard.edu/silencing/
Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy
Advancing the New Machine, a Quick Review
by Olga Werby •

It’s been a few days, and I now have some time to write down my impressions of the Advancing the New Machine Human Rights Conference held in Berkeley last week. Like all conferences, some presentations were amazing, and some not so much. But overall, Berkeley Human Rights Canter did a great job of fitting a lot of interesting speakers into a two-day program. Most of the time, there were two sessions running at the same time—I found that annoying, since I wanted to be at two place at once on several occasions! But I got to talk to many presenters and was able to download their slides. I’ve asked permission to share a few of those slides with the ICT & Human Rights group on LinkedIn, which is what I’m doing with this blog. Please note that I’m only posting what I found to be particularly interesting to me and to the members of ICT & Human Rights group. UN Global Pulse This was one of the first presentations of the conference, part of the “Ignite Talks.” The speaker was Robert Kirkpatrick, Director of UN Global Pulse. Robert talked about how cell phones can be used to monitor population’s well…
Pipsqueak Articles, Product Design Strategy, Scaffolding, Users
Advancing the New Machine UCLA Law Forum Presentation
by Olga Werby •

Today, I presented UCLA Law Forum at the Advancing the New Machine human rights conference in Berkeley. Below is an approximation of my presentation. How many of you have ever used a chair to reach that jar of tomatoes on the top shelf? I do it all the time. I’m the shortest member of my family and I use chairs as my personal hight extension. And I know I’m not alone. People are opportunists. We use products to get what we want. We subvert existing technologies to reach our own goals. From phones to cameras, from crisis mapping to photo editing, from news papers to forums, we manipulate and use tools and features to accomplish what we want, what we need. And we don’t necessarily use those tools for what they were designed for originally… As product designers, we need to be able to harness this opportunistic behavior to accomplish what we want. We want to direct crowds down the path that’s most productive and more aligned with goals of our projects. Two years ago, I came to The Soul of the Machine Conference to learn who are the players and what projects showed promise in using technology to advance…
