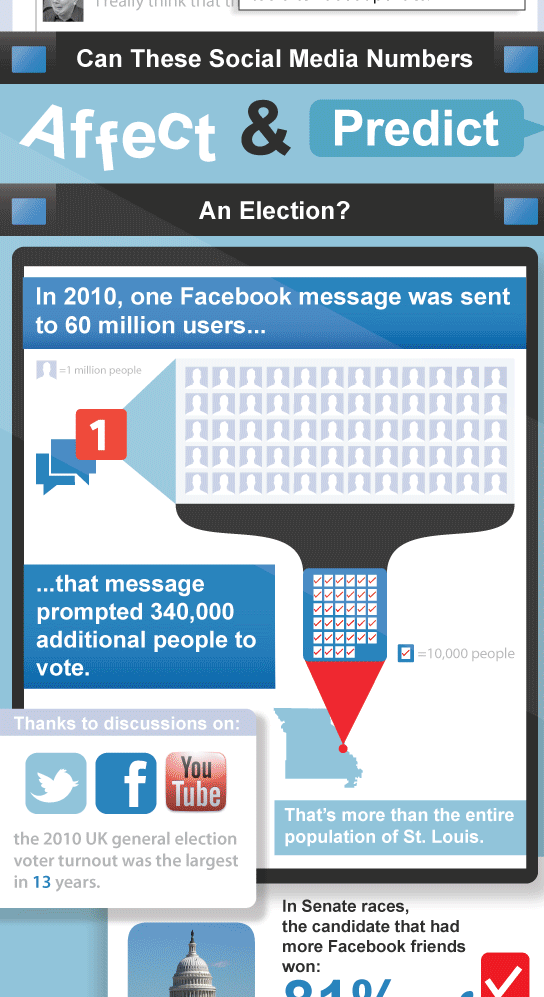
The creative folks at Open-Site.org invited me to share the following informational graphic with the readers of this blog. Anyone with a Facebook or Twitter account has probably noticed an increase in the number of political postings over the past few years. This is due, in part, to the explosive rise in social media outlets and users. But voters are not the only people who use social media; among politicians, 9 out of 10 Senators and Representatives have Twitter accounts. However, many are starting to wonder if social media is becoming less a reporter of political races and more of a predictor of the results. In Senate races, the candidate with more Facebook friends than his or her opponent has won 81% of the time. And one email sent to 60 million Facebook users prompted an additional 340,000 people to vote in the 2010 election. This infographic illustrates just how politics and social media are affecting each other.