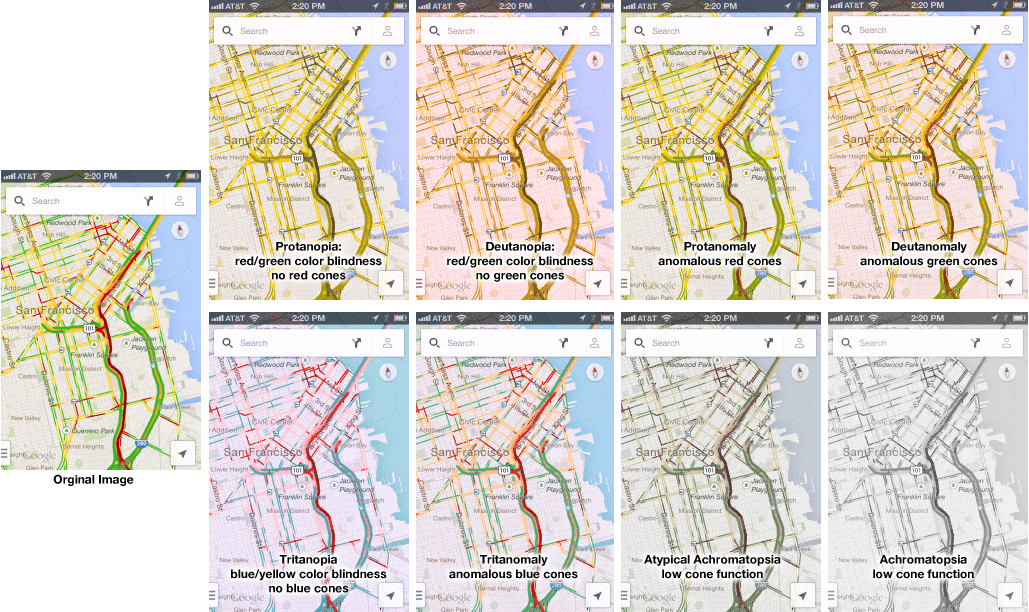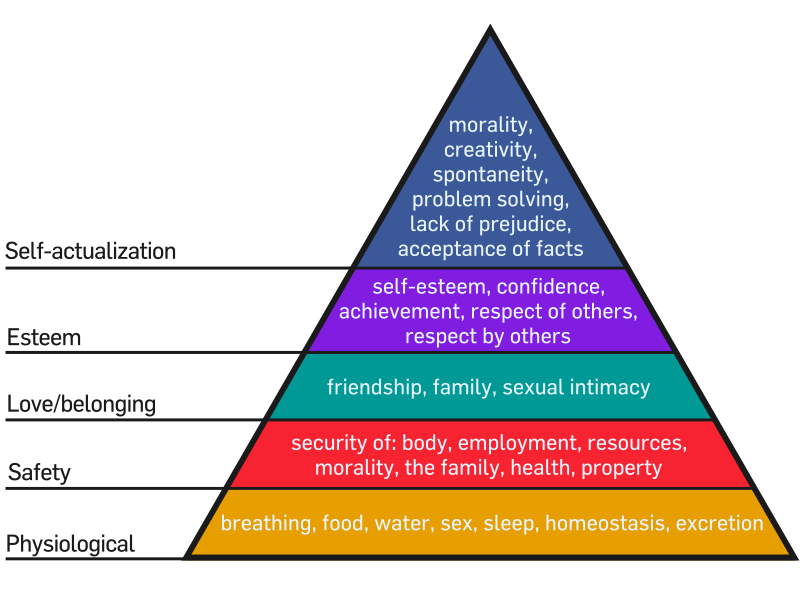
In 1943, Abraham Maslow published a paper on human motivation: “A Theory of Human Motivation.” The ideas (and diagram) from that paper have been widely used in business schools and management training programs. But these same ideas can be applied to human rights. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, signed into life by UN General Assembly on 10 December 1948, just five years after the Maslow’s publication of “A Theory of Human Motivation”, echoes the work via a set of Articles stating the rights of every human being. Physiological Needs Article 25 of The Universal Declaration of Human Rights states that everyone is entitled to the right of adequate food (and presumably water is included), housing and clothing (for homeostasis control), and medical care. The right to medical care implies to me the right to live healthy, or at least healthy to the best of ability of a particular individual. This right to medical care as a universal right of all human beings can be interpreted to mean many things. For the purposes of the comparison to the Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, it could be interpreted as every human has the right to have their physiological needs met. This could…