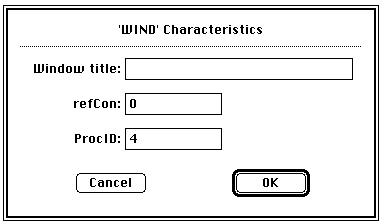
I have very strong opinions about where on the screen the OK or NEXT or SUBMIT buttons go in relation to CANCEL. Without giving it away, I’m going to walk through the design decision tree and provide a lot of references for both sides of the issue — yes, there are strong feelings about the right versus the left position choice. I’m not alone! Passive versus Active Buttons Active Buttons are the ones that advance the action to the next level. Passive ones return the users to previous state, negate the action sequence. OKAY, OK, NEXT, SUBMIT, ACCEPT, GO are all active buttons. CANCEL, BACK, PREVIOUS are action that reverse forward momentum and push the user to places they’ve been before. HELP and INFO sidetrack the user and distract from forward thrust of activity. In general, product designers want to move the users toward their goals — thus we want the perceptual focus to be on the action buttons. We want to make sure that users fist see the way forward, and then click on the right button that propels them forward to completion of the task. All distractions and side movements should be downplayed with Interface Design with the…