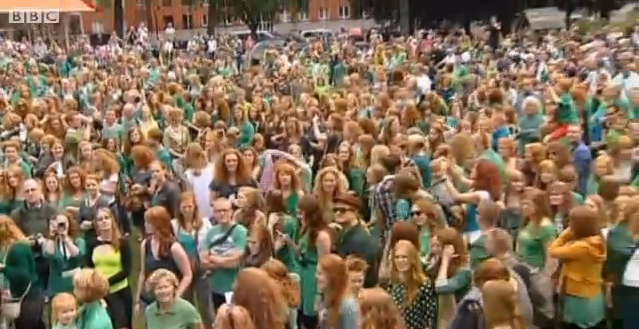
The Color of the Redhead Festival… …is NOT red! An annual festival of redheads has been taking place in Breda, Holland, was held on 3 September of this year. Almost 2000 red heads from 52 countries gathered together to share and revel in their DNA, BBC corresponded Tim Allman reported. In the sea of red, what stands out is a clear preference for color green. Somehow, the color green become the unofficial uniform of the red-headed. It’s not like they all thought: “I think everyone will be wearing green, so should I.” More likely, redheads believe they look better in green. But when every one in the group shows up in green, it strengthen the bond. Red Delegates, Blue Delegates Check out this crowd shot of the republican convention. Notice any color that stands out? How about at the democratic convention? And here’s a lighting scheme for the democratic convention: The convention organizers used color as a reenforcement of political unity for the delegates at both conventions. Using Color to Cement Group Affiliation There are certain professions that signal group membership with color: white used to be the preference for doctors and scientists working at a lab; green or blue…





