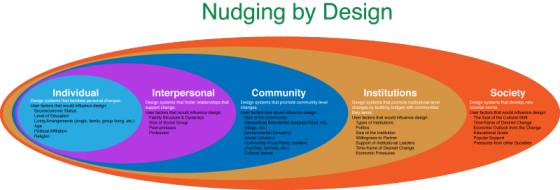
One of the events at the Sage Assembly in Paris this year was the group design sessions to try to solve “problems of the city” after the Charley attack. Paris is still in shock and the city is trying to do something to heal itself. My group, led by Arno Klein of Sage Bionetworks, was charged with finding ways of using crowdmapping to help find some interesting solutions. This was a complete blue sky session. And our ideas were presented by Arno at the Hotel De Ville in Paris. Here are my prep notes for this event. Cities generate an enormous amounts of data: parking tickets data; water consumption data; number of riders using public transportation per hour per location; etc. But most of the data stays locked within isolated databases inside frequently competitive city departments. There are several cities that are trying solve the data silos problem. Palo Alto, CA, created a city API and open-sourced all city data to allow its citizens to discover problems and develop novel solutions. One of the prevailing problems, even after the break down of data silos, is that the data is not normalized, making it very difficult to manipulate. Data normalization can…