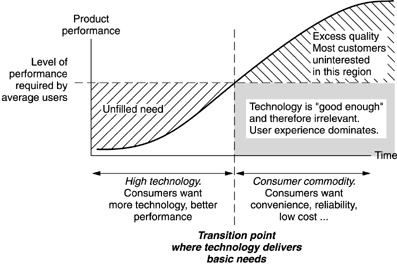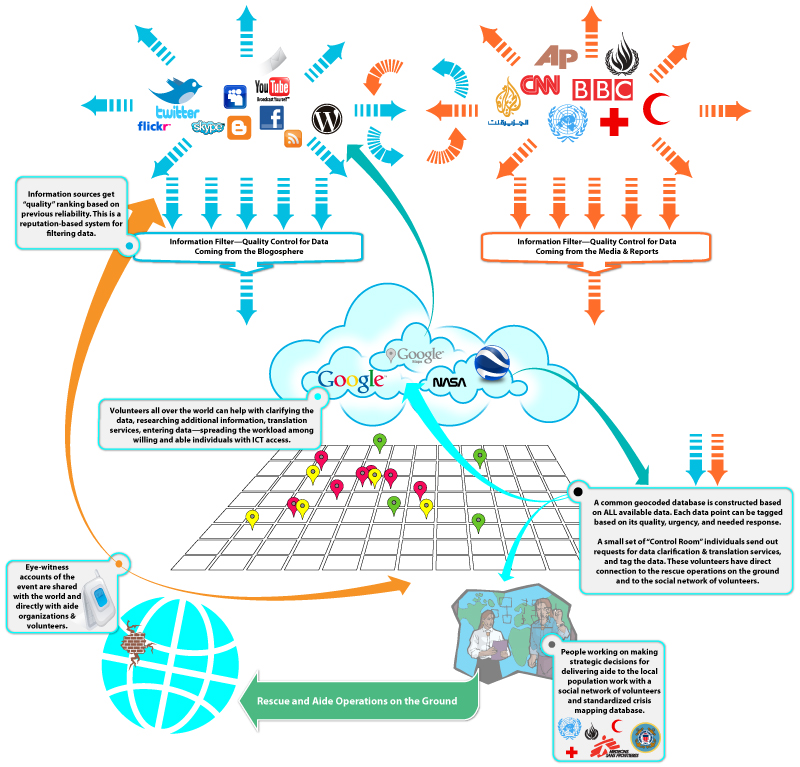
Once again, we get an early preview of the next chapter of Interaction-Design.org textbook: Activity Theory. The author of the chapter, Victor Kaptelinin, did a wonderful job of summarizing decades of research in educational psychology, cognitive science, and HCI — from Vygotsky to Moran. If you’re unfamiliar with the theories, research, and thinking that brought us to present day HCI design, this is a great place to start (and includes all of the references to the relevant literature). Adopting an activity-theoretical perspective has an immediate implication for design: it suggests that the primary concern of designers of interactive systems should be supporting meaningful human activities in everyday contexts, rather than striving for logical consistency and technological sophistication. While this chapter focuses mainly on human computer interaction (HCI), I would argue that we need to be broader: we need to focus on product design. And as always, I mean product to be interpreted in a very broad sense. We are moving rapidly into a world where everything we touch is a computing device. Today, I Twitted that my washing machine is an ICT device — the new ARM chip is small, requires very little power, and will be incorporated into everything.…